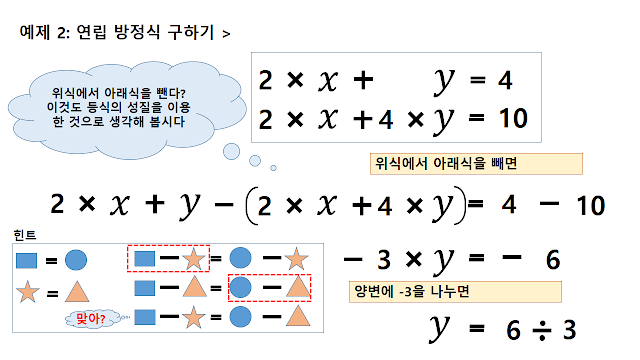
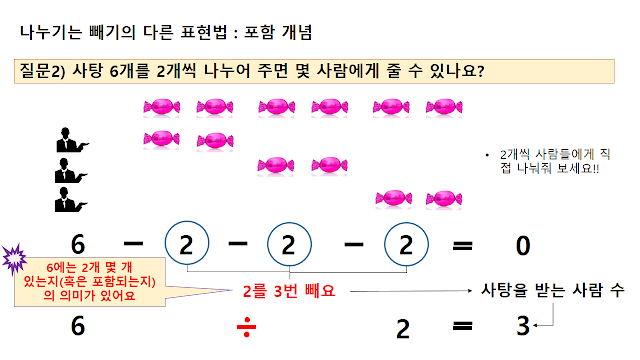
Start a blog to organize and share what you have studied alone. I mainly do theory of relativity and quantum mechanics, and also think about physics stories that elementary and junior high and high school students can understand.
2020년 11월 24일 화요일
2020년 9월 10일 목요일
(The Limits of Classical Physics-2) Derivation of Planck’s Formula (Gasiorowicz chapter 1)
< Quotation >
Robert Eisberg, Robert Resnick, “Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei, and Particles”, 1.3. LASSICAL THEORY OF CAVITY RADIATION
|
|---|
■ Planck realized that, in the circumstances that prevail for the case of blackbody radiation, the average energy of the standing waves is a function of frequency having the properties indicated by
○ This is in contrast to the law of equipartition of energy which assigns to the average energy a value independent of frequency.
■ Let us look at the origin of the equipartition law. It arises, basically, from a more comprehensive result of classical statistical mechanics called the Boltzmann distribution. Here we shall use a special form of the Boltzmann distribution
Such an abrupt change in potential is
In which P(ℇ)dℇ is the probability of finding a given entity of a system with energy in the interval between ℇ and ℇ+dℇ, when the number of energy states for the entity in that interval is independent of ℇ.
Such an abrupt change in potential is
The integrand in the numerator is the energy, ℇ, weighted by the probability that the entity will be found with this energy. The integral in the numerator can be evaluated, and the result is just the law of equipartition of energy
■ Planck's great contribution came when he realized that he could obtain the required cutoff, indicated in , if he modified the calculation leading from Pℇ to by treating the energy ℇ as if it were a discrete variable instead of as the continuous variable that it definitely is from the point of view of classical physics. Quantitatively, this can be done by rewriting in terms of a sum instead of an integral.
○ Planck assumed that the energy ℇ could take on only certain discrete values, rather than any value, and that the discrete values of the energy were uniformly distributed; that is, he took
Such an abrupt change in potential is
as the set of allowed values of the energy. Here ∆ℇ is the uniform interval between successive allowed values of the energy
○ Recapitulating, Planck discovered that he could obtain when the difference in adjacent energies ∆ℇ is small, and when∆ℇ is large. Since he needed to obtain the first result for small values of the frequency \(v\),and the second result for large values of \(v\), he clearly needed to make ∆ℇ an increasing function of \(v\). Numerical work showed him that he could take the simplest possible relation between ∆ℇ and \(v\) having this property. That is, he assumed these quantities to be proportional
Such an abrupt change in potential is
Written as an equation instead of a proportionality, this is
where h is the proportionality constant
○ The formula Planck obtained for ℇ ̅ by evaluating the summation analogous to the integral in
Sums must be used because with Planck's postulate the energy ℇ becomes a discrete variable that takes on only the values ℇ=0,hv,2hv,3hv,⋯. That is, ℇ=nhv where n=0,1,2,3,⋯
(The Limits of Classical Physics-1) Classical Derivation of Rayleigh-Jeans Formula (Gasiorowicz chapter 1)
< Reference >
I referred to Professor Joon-Gon Choi's lecture on quantum mechanics 1 at Korea University.
Robert Eisberg, Robert Resnick, “Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei, and Particles”, 1.3. LASSICAL THEORY OF CAVITY RADIATION
|
|---|
■ Theoretical research in the field of thermal radiation began in 1859 with the work of Kirchhoff, who showed that for a given λ, the ratio of the emissive power E to the absorptivity A, defined as the fraction of incident radiation of wavelength λ that is absorbed by the body, is the same for all bodies. Kirchhoff considered two emitting and absorbing parallel plates and showed from the equilibrium condition that the energy emitted was equal to the energy absorbed (for each λ), that the ratio E/A must be the same for the two plates. Soon thereafter, he observed that for a black body, defined as a surface that totally absorbs all radiation that falls on it, so that A=1, the function \(E\left( {\lambda ,T} \right)\) is a universal function.
○ The energy from the outside of the blackbody is measured in proportion to the amount of energy from the inside of the blackbody through the hole dA of the blackbody.
○ The total energy (\( \in \left( {{\rm{\lambda }},T} \right)\)) generated by the energy density inside the black body comes out through the hole dA
○ \(E\left( {{\rm{\lambda }},T} \right)\) : energy(\( \in \left( {{\rm{\lambda }},T} \right)\)) emitted per unit area(\(dA\)) per unit time (\({\rm{\Delta }}t\))
○ \(u\left( {{\rm{\lambda }},T} \right)\) : Energy density in blackbody
■ Energy Density
■ Classical Derivation of Rayleigh-Jeans Law
○ Boundary Condition
♦ Periodic boundary condition
○ The function that satisfies the periodic boundary condition is typically an oscillator.
♦ One dimension
♦ Three dimension
○ Equipartition Theorem(Robert Eisberg, Robert Resnick)
♦ The prediction comes from classical kinetic theory, and it is called the law of equipartition of energy. This law states that for a system of gas molecules in thermal equilibrium at temperature T, the average kinetic energy of a molecule per degree of freedom
♦ However, each oscillating standing wave has a total energy which is twice its average kinetic energy. This is a common property of physical systems which have a single degree of freedom that execute simple harmonic oscillations in time; familiar cases are a pendulum or a coil spring.
♦ Rayleigh assumed the classical law of equipartition energy. He said, “one dimensional waves always have 2 degrees of freedom, one for potential energy (x) and the other for kinetic energy (v). In case of electromagnetic wave, these two degree of freedom are derived from electric field and magnetic field.” ( http://www.pa.uky.edu/~kwng/phy361/class/class10.pdf )
○ degree of freedom
♦ Since k is a function of n and n is an integer, it is easy to count n. Therefore, we calculate the degrees of freedom using n.
♦ This completes the calculation except that we must multiply these results by a factor of 2. because, for each of the allowed frequencies we have enumerated, there are actually two independent waves corresponding to the two possible states of polarization of electromagnetic radiation.
2020년 9월 9일 수요일
인물로 보는 고대 수학(2) - 제논의 역설과 무한
고대 그리스 철학자 제논이 제시한 여러 문제들 중 하나를 소개합니다. 이 문제들은 최초로 무한과 관련된 내용이며 “제논의 역설"이라고 합니다. 제논의 역설은 무한에 대한 개념이 정립되는 19세기에 와서야 비로서 논리적으로 반박 이가능하게 되는데, 그 중 한 문제를 소개하면
2020년 8월 16일 일요일
인물로 보는 고대 수학(1) - 피타고라스와 무리수
기원전 570년 ~ 기원전 495년에 살았던 인물로 피타고라스에 대한 기록들은 그의 사후에 작정되었던 것으로 신뢰할 수 있는 정보가 드물다고 합니다. 피타고라스는 그를 따르는 사람들이 많아 학파를 이루었는데 그 학파를 “피타고라스 학파”라고 합니다. 피타고라스 학파는 종교집단과 같아서 신비주의 집단이었다고 합니다. 학파 사람들끼리 알게 된 내용을 함부로 외부에 알리지 못하게 하였기 때문에 피타고라스의 업적이 피타고라스가 한 것인지 그의 제자가 한 것인지 명확히 알 수가 없다고 합니다. 피타고라스 학파의 업적 중 우리에게 가장 많이 알려져 있는 것은 피타고라스의 정리입니다.
<피타고라스 정리>
피타고라스 정리는 직각삼각형 세변의 길이의 관계를 나타내는 수식입니다. 피타고라스는 증명을 길가에 깔려있는 타일을 보고 했다고 합니다. (피타고라스가 만들지 않았다는 주장도 있습니다.)
피타고라스 정리를 증명하는 방법은 1) 유클리드의 증명, 2) 삼각형의 닮은꼴을 이용한 증명, 3) 대수적 증명, 4) 가필드의 증명 외에 매우 많습니다. 이와 같이 여러 증명 중 가장 쉬운 증명을 하나 소개하겠습니다(삼각형의 닯음꼴을 이용하는 방법을 소개).
<참조>
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%94%BC%ED%83%80%EA%B3%A0%EB%9D%BC%EC%8A%A4
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%94%BC%ED%83%80%EA%B3%A0%EB%9D%BC%EC%8A%A4_%EC%A0%95%EB%A6%AC
http://weteacher.net/math/theorem/Pythagoras.htm
<피타고라스 음계>
피타고라스 정리 외에도 음악에도 관심이 많았나 봅니다. 현의 길이가 정수비를 가질 때 소리가 아름답다는 것을 발견하고 “피타고라스 음계”라는 것을 만들었다고 합니다. 음악적인 의미는 잘 모르겠지만 수학적인 의미에서 중요한 것은 정수비입니다. 이걸 조금 다르게 표현하면 정수로 이루어진 분수가 됩니다. 만물의 근원을 수로 생각하는 피타고라스 학파에게는 아름다운 조화를 만들어내는 정수비는 매우 중요한 것입니다.
<참조>
<히파수스의 무리수 발견>
무리수란 두 정수의 비로 나타낼 수 없는 수입니다. 느낌이 오시나요? “피타고라스 음계”에서 이야기 한 것처럼 정수비(=분수)가 아닌 수가 무리수입니다. 정수비(=분수)로 나타내는 수는 유리수이고 영어로 rational number입니다. 무리수는 영어로 irrational number입니다. ‘ir”이 더 있는데 유리수가 아닌 수란 의미죠. 이 무리수를 발견한 사람이 피타고라스 학파의 일원인 히파수스라는 사람입니다. 히파수스는 피타고라스 정리에 1을 대입한 후, 제곱해서 2가되는 수를 찾아 봤습니다. 그런데, 정수비로는 이런 수가 존재하지 않는 다는 것을 알게 됩니다(\({1^2} + {1^2} = 2 = {x^2},\;x = ?\)). 종교집단인 피타고라스 학파에서는 정수비가 아닌 수가 존재한다는 것을 받아 들일 수가 없었나 봅니다. 결국, 무리수의 존재를 이야기한 히파수스는 동료들에게 쫓기다 절벽에 떨어져 죽었다고 합니다. 피타고라스 학파의 일원인 히파수스가 자기의 스승이 만든 피타고라스 정리를 이용하여 무리수를 발견하고 자신의 동료들에게 죽임을 당했다고 하니 아이러니한 거 같습니다.